Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to create a new database using the PostgreSQL CREATE DATABASE statement.
PostgreSQL CREATE DATABASE statement overview #
In PostgreSQL, a database is a collection of schemas, tables, views, indexes, and other objects. PostgreSQL isolates each database from others, ensuring security.
Each PostgreSQL server can have multiple databases. You can create a new database using the CREATE DATABASE statement.
Here’s the basic syntax of the CREATE DATABASE statement:
CREATE DATABASE database_name;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)The CREATE DATABASE statement requires only the database name.
The CREATE DATABASE has many other options I’ll cover in the following tutorial.
If you create a database that already exists, you’ll encounter an error.
We’ll show you how to create a database using psql and pgAdmin tools.
Create a new database using psql #
First, open a terminal on Linux or a command prompt on Windows and connect to your local PostgreSQL using the psql command:
psql -U postgresCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)It’ll prompt you to enter the password for the postgres user. You need enter a valid password for the postgres user to connect.
Second, execute the CREATE DATABASE statement to create a new database:
CREATE DATABASE sales;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)PostgreSQL will create a new database with the name sales.
If the sales database already exists, you’ll get the following error:
ERROR: database "sales" already existsCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Third, display detailed information about the sales database by executing the following command:
\l salesCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Output:
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Locale Provider | Collate | Ctype | Locale | ICU Rules | Access privileges
-------+----------+----------+-----------------+----------------------------+----------------------------+--------+-----------+-------------------
sales | postgres | UTF8 | libc | English_United States.1252 | English_United States.1252 | | |Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Alternatively, you can retrieve database names from the pg_database view using the following query:
SELECT
datname
FROM
pg_database
WHERE
datname = 'sales';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
datname
---------
salesCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Current Database #
When connecting to a PostgreSQL using psql without specifying a database, you’re connecting to the postgres database by default. The postgres database becomes the current database.
The prompt looks like this:
postgres=#Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Alternatively, you can check the current database in psql using the \c command:
\cCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)It’ll return the following output:
You are now connected to the database "postgres" as user "postgres".Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)After creating a new database, you can switch the current database to it using the \c command:
\c database_nameCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)For example, the following command changes the current database to the sales database:
\c salesCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)The prompt will be like the following:
sales=#Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)It indicates that the current database is sales.
Create a new database using pgAdmin #
If you prefer a graphical user interface (GUI), pgAdmin is an excellent tool for managing and interacting PostgreSQL databases.
Step 1: Open pgAdmin #
- First, launch pgAdmin application.
- Second, connect to your PostgreSQL server.
Step 2: Navigate to Databases #
- First, expand the Servers section in the left sidebar.
- Second, expand your PostgreSQL server.
- Third, right-click on Databases.
- Finally, select Create > Database…

Step 3: Configure the Database #
- First, enter a name for your database in the Database input field, such as
hr. - Second, click the Save button to create the database.
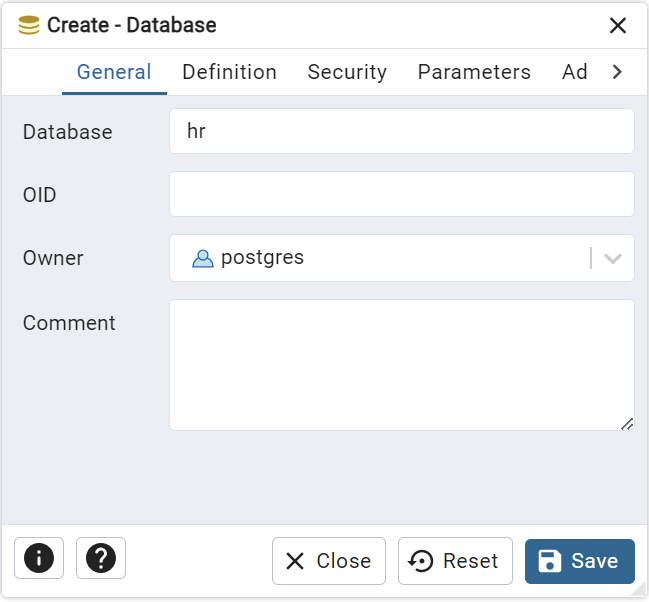
Behind the scenes, pgAdmin uses the CREATE DATABASE statement to create the hr database.
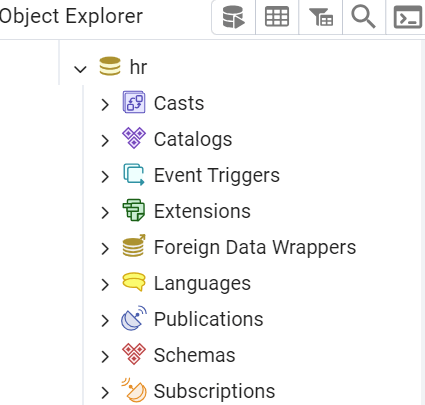
Step 4: Verify the Database #
You’ll see the new database appear under the Databases section in pgAdmin:
Database owner #
The user you use to create a database becomes the database owner. The database owner is a role (or user) that has special privileges, including:
- Full control over the database: The owner can create, alter, and modify database objects (tables, views, indexes, functions, etc.).
- Grant and revoke privileges: The owner can grant and revoke permissions on database objects to other users.
- Drop the database: Only the owner (or a superuser) can delete the database.
- Manage extensions: the owner can manage extensions within the database.
In the previous example, we used the postgres user, a superuser, to create the sales and hr databases. Therefore, the postgres user became the database owner of the sales and hr databases.
The following query returns the database names and owners:
SELECT
datname,
pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid (datdba) AS owner
FROM
pg_database
WHERE
datname IN ('sales', 'hr');Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Output:
datname | owner
---------+----------
sales | postgres
hr | postgresCode language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Note that you can change the owner of a database using the ALTER DATABASE statement.
Summary #
- Use the
CREATE DATABASEstatement to create a new database.