Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the PostgreSQL VAR_SAMP aggregate function to calculate the sample variance of a set of values.
Getting Started with the PostgreSQL VAR_SAMP aggregate function #
Given a set of values, a sample variance measures how much values differ from the average value or mean.
In statistics, mean and average are the same concept.
Sample variance is an important indicator because it reflects the spread or dispersion of the data points.
How to Calculate Sample Variance #
Here’s how you calculate the sample variance:
- First, calculate the mean of all the values.
- Next, subtract the mean from each value to find the difference (or deviation) of each value from the mean.
- Then, square each deviation to ensure all the values are positive.
- After that, sum all the squared deviations.
- Finally, divide the sum by the number of values minus one (n – 1) to get the sample variance.
Formula for Sample Variance #
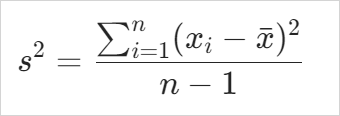
where:
- s2 is the sample variance.
- xi is each individual value.
- x̄ is the mean.
- n is the number of values in the sample.
In PostgreSQL, you can use the VAR_SAMP aggregate function to calculate the sample variance of a set of values:
SELECT VAR_SAMP(column1)
FROM table_name;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)In this syntax, the VAR_SAMP function takes all values in column1 and returns the sample variance.
The VAR_SAMP function ignores NULL in column1. It only uses non-NULL when calculating the sample variance.
If column1 has no value, i.e., no rows to aggregate, the VAR_SAMP function returns NULL.
Calculating Sample Variance for Groups #
To calculate the sample variance for groups, you can use the VAR_SAMP function with the GROUP BY clause:
SELECT column2, VAR_SAMP(column1)
FROM table_name
GROUP BY column2;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)In this syntax:
- The
GROUP BYclause divides the rows in thetable_nameby the values incolumn2into various groups. - The
VAR_SAMPfunction calculates the sample variance for values in each group.
PostgreSQL VAR_SAMP Aggregate Function Examples #
Let’s explore using the VAR_SAMP function with practical examples based on an inventory database.

Calculating the Sample Variance of Product Weight #
The following example uses the VAR_SAMP function to calculate the sample variance of weights for all products:
SELECT
VAR_SAMP(gross_weight) AS sample_variance
FROM
products;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Output:
sample_variance
----------------------
286.3391993333333333Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)The output sample variance indicates how much the products’ weights differ from the mean weight.
To make the result more readable, you can round it using the ROUND() function:
SELECT
ROUND(VAR_SAMP(gross_weight),2) AS sample_variance
FROM
products;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Output:
sample_variance
-----------------
286.34Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Calculating the Sample Variance of Product Weight by Category #
The following example uses the VAR_SAMP function with the GROUP BY clause to calculate the sample variance of product weights by category:
SELECT
category_id,
ROUND(VAR_SAMP(gross_weight), 5) AS sample_variance
FROM
products
GROUP BY
category_id;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Output:
category_id | sample_variance
-------------+-----------------
11 | 0.38589
9 | 65.78045
3 | 0.00436
5 | 0.00000
4 | 0.05120
6 | 0.00020
12 | 29.79920
8 | 32.41350Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)In this example:
- First, the
GROUP BYclause divides the products by thecategory_idinto groups. - The
VAR_SAMPfunction calculates the sample variance for gross weights in each group.
If you want to retrieve the category name, you can join the products table with the categories table:
SELECT
category_name,
ROUND(VAR_SAMP(gross_weight), 5) AS sample_variance
FROM
products
JOIN categories USING (category_id)
GROUP BY
category_name;Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)Output:
category_name | sample_variance
---------------+-----------------
Desktops | 29.79920
Televisions | 32.41350
Accessories | 0.00000
Tablets | 0.05120
Wearables | 0.00020
Laptops | 0.38589
Smartphones | 0.00436
Audio Systems | 65.78045Code language: PostgreSQL SQL dialect and PL/pgSQL (pgsql)The output shows the variability of product weights within each category. The categories with higher sample variance might have a broader range of product weights.
Summary #
- Use the PostgreSQL
VAR_SAMPaggregate function to calculate the sample variance of a set of values.